Pointers in C Language: Program To Add Two Numbers Using Pointers
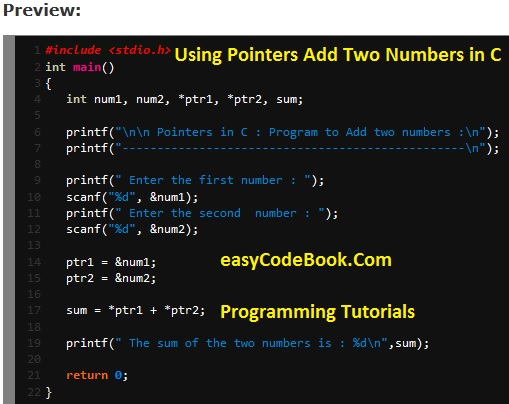
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int num1, num2, *ptr1, *ptr2, sum; printf("\n\n Pointers in C : Program to Add two numbers :\n"); printf("-------------------------------------------------\n"); printf(" Enter the first number : "); scanf("%d", &num1); printf(" Enter the second number : "); scanf("%d", &num2); ptr1 = &num1; ptr2 = &num2; sum = *ptr1 + *ptr2; printf(" The sum of the two numbers is : %d\n",sum); return 0; }
SAMPLE OUTPUT:
Pointers in C : Program to Add two numbers :
————————————————-
Enter the first number : 12
Enter the second number : 13
The sum of the two numbers is : 25
Explanation of Using Pointers Add Two Numbers Program
#include <stdio.h> int main() { /* First of all we declare 2 int variables num1 and num2. Two pointer variables ptr1 and ptr 2 are also declared with a * before identifier. These are pointers to integer. */ int num1, num2, *ptr1, *ptr2, sum; /* Here we display some messages using printf() */ printf("\n\n Pointers in C : Program to Add two numbers :\n"); printf("-------------------------------------------------\n"); /* Display prompt to enter a number and get input from the user. */ printf(" Enter the first number : "); scanf("%d", &num1); printf(" Enter the second number : "); scanf("%d", &num2); /* Assign address of num1 variable to pointer variable ptr1 with the help of & operator. Similarly, put address of num2 variable in pointer variable ptr2 with the help of & operator. */ ptr1 = &num1; ptr2 = &num2; /*Now add two integer variables using pointers and dereferencing operator * before pointer name. * is also called indirection operator. *ptr1 will refer to the value of num1 variable. Because ptr1 has the address of num1. Similarly, *ptr2 will refer to the value of num2. */ sum = *ptr1 + *ptr2; /* Print the sum of two variables using printf() */ printf(" The sum of the two numbers is : %d\n",sum); return 0; }
![]()