Learn Data Cleaning in Data Frames –
What is Data Cleaning?
Data cleaning is a crucial step in the data analysis process that involves identifying and handling errors, inconsistencies, and missing values in a dataset.
Learn Data Cleaning in Data Frames
Data Cleaning in Data Frames
In the context of data frames, which are widely used in data analysis libraries like Pandas (Python) or R, data cleaning typically involves operations to clean, preprocess, and transform the data into a more usable and accurate form.
Data Cleaning Operations in Python Pandas
Here are some common data cleaning operations in Pandas:
- Handling Missing Values:
df.isnull(): Returns a DataFrame of the same shape as the input withTrueandFalseindicating missing values.df.dropna(): Drops rows with missing values.df.fillna(value): Fills missing values with a specified value.
- Removing Duplicates:
df.duplicated(): Returns a boolean series indicating duplicate rows.df.drop_duplicates(): Drops duplicate rows.
- Changing Data Types:
df.astype(): Converts the data type of a column.
- Renaming Columns:
df.rename(columns={'old_name': 'new_name'}): Renames columns.
- String Operations:
df.str.upper(),df.str.lower(): Converts strings to uppercase or lowercase.
- Handling Outliers:
- Identify and handle outliers using statistical methods.
These are just a few examples, and the specific operations you need may depend on the characteristics of your dataset. Always explore the data first and tailor your cleaning process accordingly.
I’ll provide an example using Python with the Pandas library.
Python Example using Pandas
import pandas as pd
# Create a sample DataFrame
data = {'Name': ['John', 'Jane', 'Bob', 'Alice', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 22, None, 35],
'Salary': [50000, 60000, 45000, 55000, 70000],
'Gender': ['Male', 'Female', 'Male', 'Female', 'Male']}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Display the original DataFrame
print("Original DataFrame:")
print(df)
print()
# Check for missing values
print("Missing Values:")
print(df.isnull())
print()
# Handle missing values
df['Age'].fillna(df['Age'].mean(), inplace=True)
# Drop rows with missing values
df.dropna(inplace=True)
# Display the cleaned DataFrame
print("Cleaned DataFrame:")
print(df)
In this example, we created a sample DataFrame with missing values in the ‘Age’ column. The data cleaning steps include checking for missing values (df.isnull()), filling missing values with the mean of the column (df[‘Age’].fillna(df[‘Age’].mean(), inplace=True)), and dropping rows with missing values (df.dropna(inplace=True)).
Output
Let’s go through the output step by step for the provided example code:
import pandas as pd
# Create a sample DataFrame
data = {'Name': ['John', 'Jane', 'Bob', 'Alice', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 22, None, 35],
'Salary': [50000, 60000, 45000, 55000, 70000],
'Gender': ['Male', 'Female', 'Male', 'Female', 'Male']}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Display the original DataFrame
print("Original DataFrame:")
print(df)
print()
Output
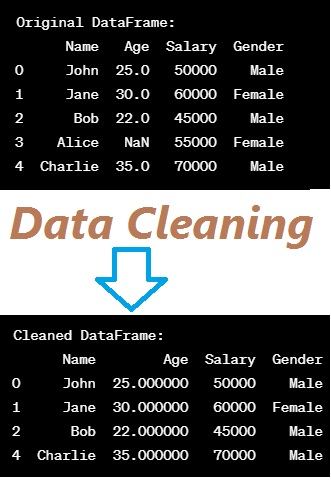
Original DataFrame:
Name Age Salary Gender
0 John 25.0 50000 Male
1 Jane 30.0 60000 Female
2 Bob 22.0 45000 Male
3 Alice NaN 55000 Female
4 Charlie 35.0 70000 Male
The original DataFrame contains missing values in the ‘Age’ column.
# Check for missing values
print("Missing Values:")
print(df.isnull())
print()
Output
Missing Values:
Name Age Salary Gender
0 False False False False
1 False False False False
2 False False False False
3 False True False False
4 False False False False
This shows the boolean DataFrame where True represents missing values.
# Handle missing values
df['Age'].fillna(df['Age'].mean(), inplace=True)
# Drop rows with missing values
df.dropna(inplace=True)
# Display the cleaned DataFrame
print("Cleaned DataFrame:")
print(df)
Output
Cleaned DataFrame:
Name Age Salary Gender
0 John 25.000000 50000 Male
1 Jane 30.000000 60000 Female
2 Bob 22.000000 45000 Male
4 Charlie 35.000000 70000 Male
The cleaned DataFrame now has missing values filled with the mean of the ‘Age’ column, and the row with a missing value has been dropped.
![]()