Python PyQt Calculator GUI Program –
This program is a PyQt-based calculator application that provides a graphical user interface (GUI) for performing basic arithmetic operations and includes a “Square Root” button (SQRT) to calculate the square root of a number.
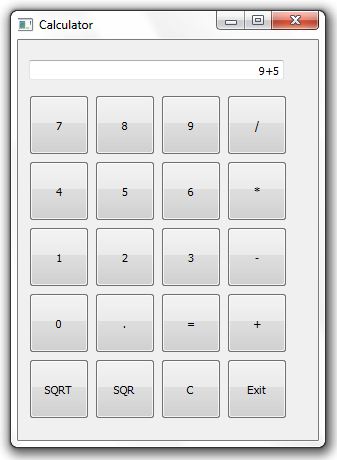
Here’s a breakdown of the program’s functionality and structure:
- Importing Required Libraries:
- The program starts by importing the necessary libraries, including
sysfor system-related functionality and the PyQt5 libraries for creating the GUI components. - It also imports the
sqrtfunction from themathmodule to handle square root calculations.
- The program starts by importing the necessary libraries, including
- CalculatorApp Class:
- The
CalculatorAppclass is defined as a subclass ofQWidget, which is the base class for all GUI objects in PyQt.
- The
- Constructor (
__init__Method):- The
__init__method sets up the initial state and GUI components of the application. - It calls the
initUImethod to create the user interface and initializes an emptyexpressionstring to store the user’s input.
- The
- initUI Method:
- The
initUImethod is responsible for creating the graphical user interface of the calculator. - It sets the window title to “Calculator” and defines the window’s initial size and position.
- It creates two layout managers:
text_box_layout(for the text input box) andbutton_grid(for the calculator buttons). - Inside
text_box_layout, aQLineEditwidget (text input box) is created, which displays the expression and results. The text box is right-aligned and has a fixed width of 255 pixels. - The calculator buttons are defined in the
button_labelslist, which includes digits, arithmetic operators, and special buttons like “SQRT” and “C.” - Buttons are organized in a 4×4 grid layout, and each button is connected to the
button_clickmethod when clicked. - An “Exit” button is added at the bottom of the grid.
- The
- button_click Method:
- The
button_clickmethod is invoked when any calculator button is clicked. - It identifies which button was clicked using the
sendermethod. - If the button is “=”, it evaluates the expression and displays the result in the text input box. If it’s “C,” it clears the expression.
- If it’s “SQR,” it calculates the square of the current expression and displays the result.
- If it’s “SQRT,” it calculates the square root of the number in the expression and displays the result.
- For other buttons (digits and operators), it appends the clicked button’s text to the expression in the text input box.
- The
- Main Block:
- The program’s entry point is the
if __name__ == '__main__':block. - An instance of the
QApplicationis created, which is required to start the PyQt application. - An instance of the
CalculatorAppclass is created, and the GUI is displayed usingcalculator.show(). - The application enters its main event loop with
app.exec_(), allowing users to interact with the calculator until it is closed.
- The program’s entry point is the
Overall, this program creates a simple calculator GUI with basic arithmetic operations and the ability to calculate square roots, providing a user-friendly interface for performing mathematical calculations.
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QGridLayout, QPushButton, QLineEdit, QVBoxLayout
from PyQt5.QtCore import Qt
from math import sqrt # Import the sqrt function from the math module
class CalculatorApp(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.initUI()
self.expression = ""
def initUI(self):
self.setWindowTitle('Calculator')
self.setGeometry(100, 100, 300, 400)
text_box_layout = QVBoxLayout()
button_grid = QGridLayout()
self.result_box = QLineEdit(self)
self.result_box.setReadOnly(True)
self.result_box.setAlignment(Qt.AlignRight) # Align text to the right
self.result_box.setFixedWidth(255) # Set a fixed width for the QLineEdit
text_box_layout.addWidget(self.result_box)
# Create buttons for digits, operators, and functions
button_labels = [
'7', '8', '9', '/',
'4', '5', '6', '*',
'1', '2', '3', '-',
'0', '.', '=', '+',
'SQRT', 'SQR', 'C'
]
row, col = 0, 0
for label in button_labels:
button = QPushButton(label, self)
button.clicked.connect(self.button_click)
button.setFixedSize(60, 60) # Set button size
button_grid.addWidget(button, row, col)
col += 1
if col > 3:
col = 0
row += 1
exit_button = QPushButton('Exit', self)
exit_button.clicked.connect(self.close)
exit_button.setFixedSize(60, 60) # Set exit button size
button_grid.addWidget(exit_button, row, col, 1, 2) # Span two columns
text_box_layout.addLayout(button_grid)
self.setLayout(text_box_layout)
def button_click(self):
sender = self.sender()
text = sender.text()
if text == '=':
try:
result = eval(self.expression)
self.result_box.setText(str(result))
except Exception as e:
self.result_box.setText("Error")
print(e)
elif text == 'C':
self.expression = ""
self.result_box.clear()
elif text == 'SQR':
try:
result = eval(self.expression)
result = result * result
self.result_box.setText(str(result))
except Exception as e:
self.result_box.setText("Error")
print(e)
elif text == 'SQRT':
try:
num = float(self.expression)
result = sqrt(num)
self.result_box.setText(str(result))
except Exception as e:
self.result_box.setText("Error")
print(e)
else:
self.expression += text
self.result_box.setText(self.expression)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
calculator = CalculatorApp()
calculator.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
![]()